When we watch a movie today, we often see things that don’t exist in real life — flying cars, monsters, exploding planets, superheroes, magical worlds, and more. These moments feel real on screen, but behind the scenes, they’re created with the help of movie effects.
Three common types of effects used in films are VFX (Visual Effects), CGI (Computer-Generated Imagery), and Practical Effects. While they often work together, they are not the same thing. In this article, we’ll explore what each one means, how they are used, and why understanding the difference is important — both for filmmakers and for movie lovers.
What Is VFX?
VFX, or Visual Effects, is a broad term that includes all kinds of visual changes made to a film after the live action has been shot. These effects are added in post-production using computers. VFX can be used to:
- Add a background that wasn’t really there
- Show something that’s impossible to film in real life
- Combine two different shots into one scene
- Create large-scale scenes like battles or city destruction
Think about scenes in Marvel movies where superheroes fly through the air or entire alien cities are shown. Those visuals were added later using VFX.
So, when you hear “VFX,” think of it as the big umbrella under which many visual tricks live — including CGI.
What Is CGI?
CGI, or Computer-Generated Imagery, is one of the most popular tools used in VFX. CGI is the process of creating images and animations using computer software.
For example:
- The dinosaurs in Jurassic World
- The Na’vi characters in Avatar
- The talking animals in The Jungle Book remake
These are all examples of CGI. These images are built from scratch on a computer and then placed into the film, often blending with real footage. CGI can be used for creating characters, settings, objects, or even crowds.
In short:
CGI is a part of VFX. It is the digital creation part, while VFX includes other post-production techniques as well.
What Are Practical Effects?
Practical effects are effects made physically, on set, in real time — without the use of computer graphics. These are real things built and shot with the camera, such as:
- Explosions using real fire
- Makeup and prosthetics for monsters or injuries
- Miniature models of buildings or spaceships
- Fake blood, smoke, or rain
Movies like Mad Max: Fury Road and The Dark Knight are known for using practical effects. In Fury Road, many of the stunts and explosions were real. It adds a gritty, realistic feeling that audiences love.
Practical effects have been used since the early days of cinema and are still important today, especially when filmmakers want authenticity.
- An actor wears a green suit (practical setup)
- The background is a green screen (VFX environment)
- A monster is added using CGI
- Then, post-production artists blend everything to make it look seamless
This mix helps save time, money, and allows for scenes that can’t be done safely or easily in real life.
Let’s look at a few famous movies to see how they blend these effects:
- Inception: Used practical effects for the rotating hallway scene and VFX for the folding city.
- The Lord of the Rings: Combined miniature models, CGI for Gollum, and VFX to create epic battle scenes.
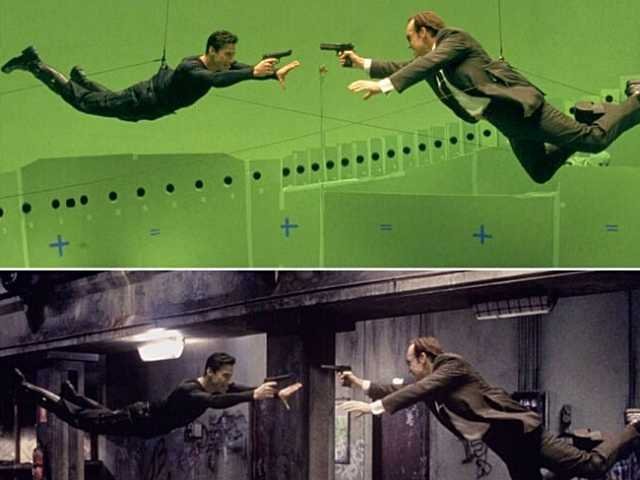
- The Matrix: Used bullet-time (a camera trick) with VFX enhancements.
The Pros and Cons of Each
Practical Effects
Pros:
- Feels real and grounded
- Good for actors to interact with
- No need for heavy post-production
Cons:
- Can be costly or dangerous (like explosions or stunts)
- Hard to redo if a mistake is made
- Limited by physics and safety
CGI
Pros:
- Allows anything to be created — no limits
- Easy to edit or change
- Great for fantasy, sci-fi, and animation
Cons:
- Can look fake if overused or badly done
- Requires skilled artists and high budget
- Can feel cold or artificial if not balanced
VFX
Pros:
- Covers everything from digital touch-ups to large scenes
- Lets filmmakers fix problems after shooting
- Useful for both small and big-budget films
Cons:
- Can delay the film if VFX work takes too long
- May increase the budget if not planned well
Why It Matters
Understanding these terms helps us see the hard work that goes into filmmaking. It’s not just about cameras and actors. It’s about building worlds, creating emotions, and pushing the limits of imagination.
Also, as audiences, we can better appreciate the creativity behind what we see on screen. Next time you watch a film, notice how these different effects are used. Did they feel real? Did they serve the story? Or did it feel too fake?
For filmmakers, knowing when to use each type of effect is crucial. Sometimes, practical effects give the scene a more raw and honest look. Sometimes, CGI helps achieve the impossible. And VFX ties it all together.
The Future of Effects in Films
With new technology like virtual production (used in The Mandalorian), the lines between real and digital are blurring. Real-time computer graphics, LED walls, and motion capture are changing how movies are made. Filmmakers can now see CGI environments in real time while filming — a mix of practical and digital working together like never before.
As audiences become more visually aware, there’s also a growing trend to bring back more practical effects. Viewers often connect better with real explosions, real sets, and handmade props. Filmmakers like Christopher Nolan and Denis Villeneuve are known for finding this balance.
Final Thoughts
VFX, CGI, and practical effects each play a special role in movies. They help create magic on screen, and when used well, they make us believe in anything — from superheroes flying to dinosaurs walking the earth.
But the best movies don’t just rely on one kind of effect. They use the right tool for the right moment. It’s not about flashy visuals — it’s about serving the story.
Whether you’re a filmmaker, a film student, or just a movie lover, understanding these effects can help you enjoy and respect cinema even more.